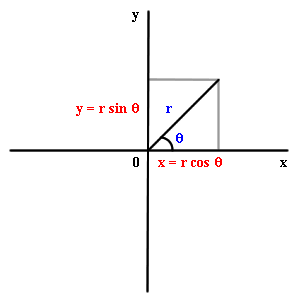|
A 2-vector (x,y) can be described by two numbers that
are not coefficients in a sum: its length, and the angle its
vector makes with the x axis. The first of these is usually
written as r, the second as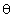 . .
These parameters obey 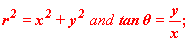
the inverse relations are 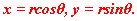
r and 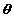 are
called polar coordinates. are
called polar coordinates.
Calculating the angle theta in polar coordinates is
a bit tricky; the obvious thing to try is atan (y, x) but
that is defined only between 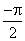 and and
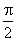 ,
while ,
while  has a domain of size 2
has a domain of size 2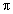 .
Here is something that works: .
Here is something that works: 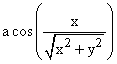 *
if(y < 0, -1, 1). *
if(y < 0, -1, 1).
This gives theta in the range - to
to  .
If you want it to have range 0 to 2 .
If you want it to have range 0 to 2 you can add if(y < 0,8 * atan(1), 0) to it.
you can add if(y < 0,8 * atan(1), 0) to it.
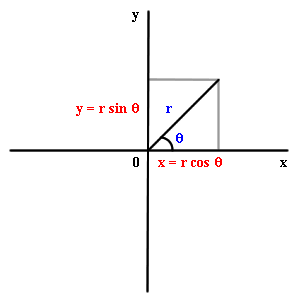
|
 |

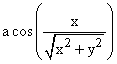 *
if(y < 0, -1, 1).
*
if(y < 0, -1, 1).