2-003js07.jpg
Description:
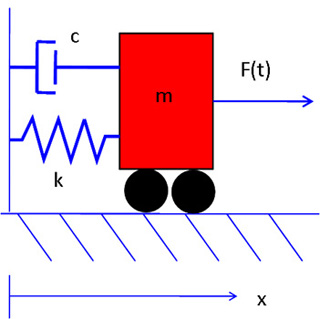
A moving cart attached to a wall by a spring and a dashpot. The equations of motion for every 1-degree-of-freedom system can be linearized around the equilibrium points to the second order differential equation that describes this system. Thus, understanding the free response and selected forced responses for this system can give deep insight into the stability of the equilibrium points and the behavior of a large number of systems. See Lectures 20 and 21 and Recitation 11 for more information. (Image courtesy of MIT OpenCourseWare.)
file
60 kB
2-003js07.jpg
Alt text:
A diagram of a moving cart attached to a wall by a spring and a dashpot.
Caption:
A moving cart attached to a wall by a spring and a dashpot. The equations of motion for every 1-degree-of-freedom system can be linearized around the equilibrium points to the second order differential equation that describes this system. Thus, understanding the free response and selected forced responses for this system can give deep insight into the stability of the equilibrium points and the behavior of a large number of systems. See Lectures 20 and 21 for more information. (Image by MIT OCW.)
Course Info
As Taught In
Spring
2007
Level
Learning Resource Types
assignment
Problem Sets
grading
Exams
notes
Lecture Notes









