Course Description
Surveys general principles and specific examples of motor control in biological systems. Emphasizes the neural mechanisms underlying different aspects of movement and movement planning. Covers sensory reception, reflex arcs, spinal cord organization, pattern generators, muscle function, locomotion, eye movement, and …
Surveys general principles and specific examples of motor control in biological systems. Emphasizes the neural mechanisms underlying different aspects of movement and movement planning. Covers sensory reception, reflex arcs, spinal cord organization, pattern generators, muscle function, locomotion, eye movement, and cognitive aspects of motor control. Functions of central motor structures including cerebellum, basal ganglia, and cerebral cortex considered. Cortical plasticity, motor learning and computational approaches to motor control, and motor disorders are discussed.
Learning Resource Types
assignment
Presentation Assignments
assignment
Written Assignments
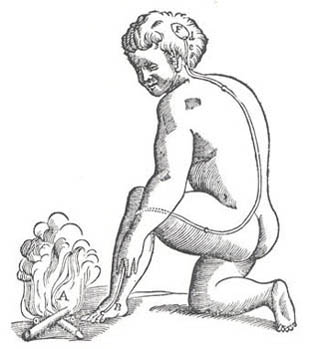
Descartes’ concept of the withdrawal reflex. (René Descartes. L’Homme de Rene Descartes. Paris: Charles Angot, 1664. Courtesy of the French National Ministry of Education.)










