Course Description
This course examines signals, systems and inference as unifying themes in communication, control and signal processing. Topics include input-output and state-space models of linear systems driven by deterministic and random signals; time- and transform-domain representations in discrete and continuous time; group …
This course examines signals, systems and inference as unifying themes in communication, control and signal processing. Topics include input-output and state-space models of linear systems driven by deterministic and random signals; time- and transform-domain representations in discrete and continuous time; group delay; state feedback and observers; probabilistic models; stochastic processes, correlation functions, power spectra, spectral factorization; least-mean square error estimation; Wiener filtering; hypothesis testing; detection; matched filters.
Course Info
Learning Resource Types
grading
Exam Solutions
grading
Exams
menu_book
Open Textbooks
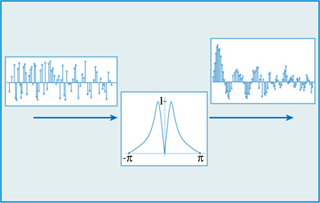
Spectral shaping of a white-noise signal. (Image by MIT OpenCourseWare. Courtesy of Prof. Alan Oppenheim and Prof. George Verghese.)










