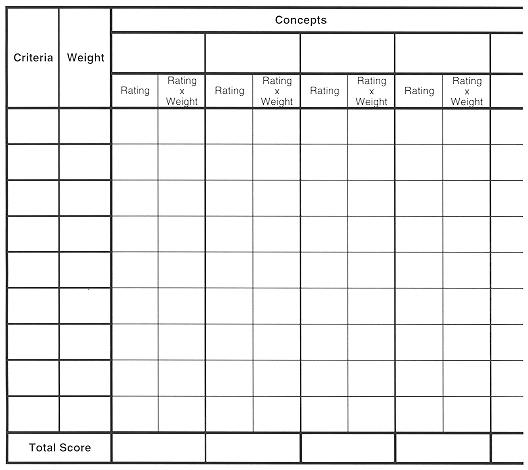
General Design Process
- General Design Process
- Understand Problem
- Conceptual Design
- Embodiment Design
- Detail Design
- Prototype and Testing
- Completion (Implementation)
What is Design
- Creative
- Synthesis
- No Unique Solution/Open Ended Problem
- Collaboration in a Team
Learning of Design
- Problem Formulation is as Important as Problem Solution
- Do Design
- Design Process and Tools
(CE)E - Design Sequence
(with selected feedback cycles)
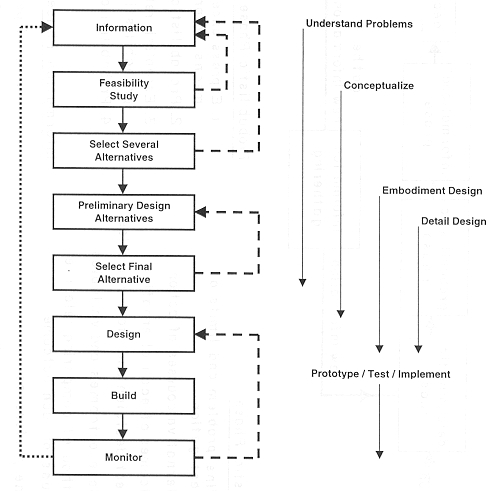
The Decision Analysis Cycle
(after Stael von Holstein, 1973)
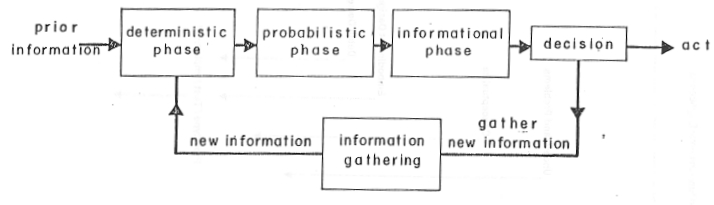
| Deterministic Phase | Probabilistic Phase |
| 1. Define Problem and Limits of Investigation | 1. Express Uncertainty in Variables by Means of Probabilities |
| 2. Alternative Courses of Action | 2. Probabilistic Model |
| 3. Outcomes of Each Alternative | 3. Establish Relative Value of Probabilistic Outcomes |
| 4. Select Decision and State Variables | 4. Probabilistic Sensitivity Analysis |
| 5. Relate Outcomes and Variables | |
| 6. Time Preference | Information Phase |
| 7. Dominated Alternatives Eliminated | 1. Value of Perfect Information |
| 8. Sensitivity of Outcome to Variables | 2. Evaluate Various Information Collection Schemes |
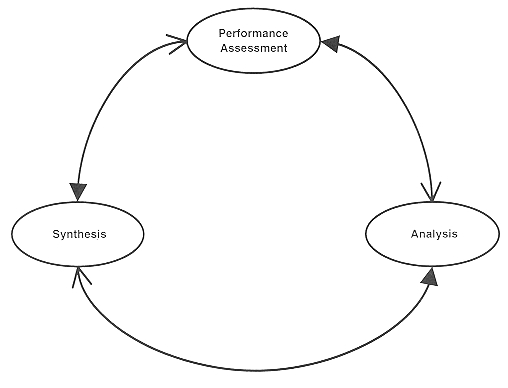
Design Process
The “Design Circle”
The “Design Spiral”
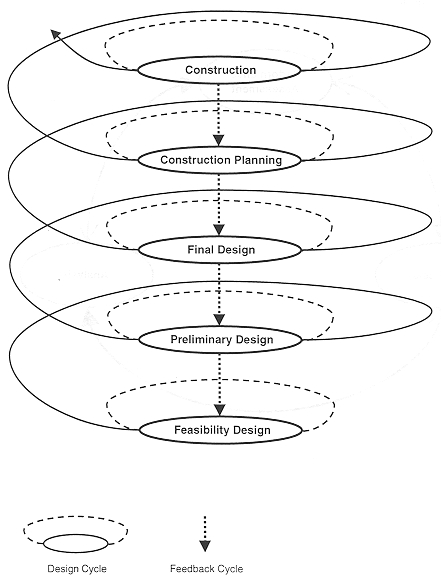
Pugh Chart
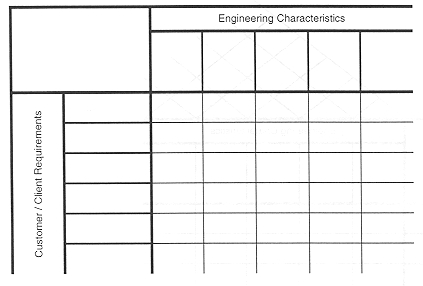
Pugh Chart / House of Quality
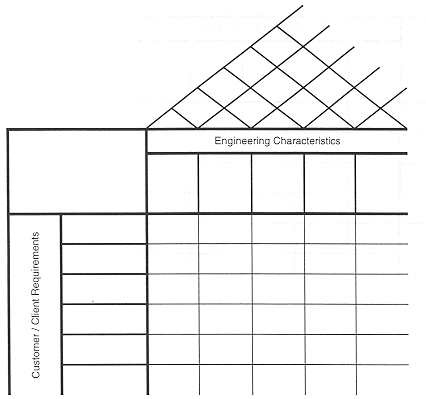
Screening Matrix
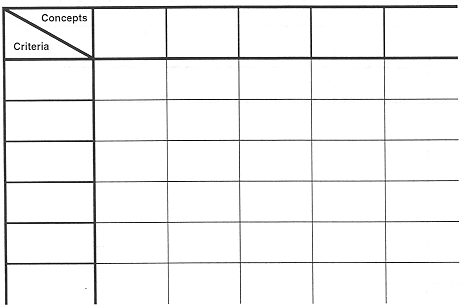
Scoring Matrix