Course Description
This course introduces the competition between energetics and disorder that underpins materials thermodynamics. Classical thermodynamic concepts are presented in the context of phase equilibria including phase transformations, phase diagrams, and chemical reactions. The course also covers computerized thermodynamics …
This course introduces the competition between energetics and disorder that underpins materials thermodynamics. Classical thermodynamic concepts are presented in the context of phase equilibria including phase transformations, phase diagrams, and chemical reactions. The course also covers computerized thermodynamics and provides an introduction to statistical thermodynamics.
Course Info
Instructor
Departments
Learning Resource Types
theaters
Demonstration Videos
edit_note
Editable Files
Instructor Insights
notes
Lecture Notes
theaters
Lecture Videos
assignment
Presentation Assignments
assignment
Problem Sets
auto_stories
Readings
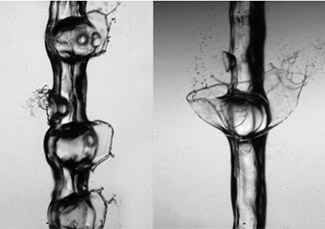
These images capture the moment pressurized jets of carbon dioxide hit normal atmospheric pressure and instantly change state to gas. Because liquid carbon dioxide cannot exist at pressures lower than 5.11 atm, solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublimes directly to vapor at normal atmosphere. (Images by Lena RUB. Source: Wikimedia Commons. License: CC BY-SA. Cropped from original.)










