Course Description
This course is a survey of perceptual and cognitive aspects of the psychology of music, with special emphasis on underlying neuronal and neurocomputational representations and mechanisms. Basic perceptual dimensions of hearing (pitch, timbre, consonance/roughness, loudness, auditory grouping) form salient qualities, …
This course is a survey of perceptual and cognitive aspects of the psychology of music, with special emphasis on underlying neuronal and neurocomputational representations and mechanisms. Basic perceptual dimensions of hearing (pitch, timbre, consonance/roughness, loudness, auditory grouping) form salient qualities, contrasts, patterns and streams that are used in music to convey melody, harmony, rhythm and separate voices. Perceptual, cognitive, and neurophysiological aspects of the temporal dimension of music (rhythm, timing, duration, temporal expectation) are explored. Special topics include comparative, evolutionary, and developmental psychology of music perception, biological vs. cultural influences, Gestaltist vs. associationist vs. schema-based theories, comparison of music and speech perception, parallels between music cognition and language, music and cortical action, and the neural basis of music performance.
Course Info
Instructor
Departments
Learning Resource Types
notes
Lecture Notes
assignment_turned_in
Problem Set Solutions
assignment
Problem Sets
group_work
Projects
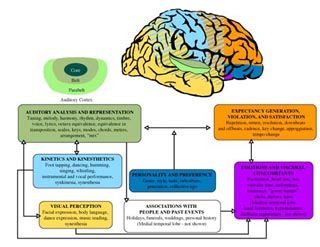
Areas of the brain that may be involved in different aspects of music perception and performance. (Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare, adapted from Tramo, Mark J. “Music of the Hemispheres.” Science 291, no. 5501 (January 5, 2001): 54-56.










