(S) = Supplemental notes.
| LEC # | TOPICS | LECTURE NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | General information | (PDF) |
| 1 | Matrices are useful in spectroscopic theory | (PDF) |
| 1 (S) | Spectroscopic notation, good quantum numbers, perturbation theory and secular equations, non-orthonormal basis sets, transformation of matrix elements of any operator into perturbed basis set | (PDF) |
| 2 | Coupled harmonic oscillators: truncation of an infinite matrix | (PDF) |
| 2 (S) | Matrix solution of harmonic oscillator problem, derivation of heisenberg equation of motion, matrix elements of any function of X and P | (PDF) |
| 3 | Building an effective hamiltonian | (PDF) |
| 3 (S) | Anharmonic oscillator, vibration-rotation interaction, energy levels of a vibrating rotor | (PDF) |
| 4 | Atoms: 1e- and alkali | (PDF) |
| 5 | Alkali and many e- atomic spectra | (PDF) |
| 6 | Many e- atoms | (PDF) |
| 7 | How to assign an atomic spectrum | (PDF) |
| 8 | The Born-Oppenheimer approximation | (PDF) |
| 8 (S) | Excerpts from the spectra and dynamics of diatomic molecules | (PDF) ( Field, R. W., and H. Lefebvre-Brion. The Spectra and Dynamics of Diatomic Molecules. Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press, 2004. ISBN: 9780124414556. Courtesy of Elsevier. Used with permission.) |
| 9 | The Born-Oppenheimer approach to transitions | (PDF) |
| 10 | The Born-Oppenheimer approach to transitions II | (PDF) |
| 11 | Pictures of spectra and notation | (PDF) |
| 12 | Rotational assignment of diatomic electronic spectra I | (PDF) |
| 13 | Laser schemes for rotational assignment first lines for Ω’, Ω" assignments | (PDF) |
| 14 |
Definition of angular momenta and | A α MA > Evaluation of ĤROT |
(PDF) |
| 14 (S) | Rotation and angular momenta | (PDF) |
| 15 | 2∏ and 2∑ matrices | (PDF) |
| 16 | Parity and e/f basis for 2∏, 2∑± | (PDF) |
| 17 | Hund’s cases: 2∏, 2∑± examples | (PDF) |
| 17 (S) | Energy level structure of 2∏ and 2∑ states, matrix elements for 2∏ and 2∑ including ∏ ~ ∑ perturbation, parity | (PDF) |
| 18 | Perturbations | (PDF) |
| 18 (S) | A model for the perturbations and fine structure of the ∏ states of CO, factorization of perturbation parameters, the electronic perturbation parameters | (PDF) |
| 19 | Second-order effects | (PDF) |
| 19 (S) | Second-order effects: centrifugal distortion and Λ-doubling | (PDF) |
| 20 | Transformations between basis sets: 3-j, 6-j, and Wigner-Eckart theorem | (PDF) |
| 21 | Construction of potential curves by the Rydberg-Klein-Rees method (RKR) | (PDF) |
| 22 | Rotation of polyatomic molecules I | (PDF) |
| 22 (S) | Energy levels of a rigid rotor, energy levels of an asymmetric rotor | (PDF) |
| 23 | Asymmetric top | (PDF) |
| 23 (S) | Energy levels of a rigid rotor, energy levels of an asymmetric rotor | (PDF) |
| 24 | Pure rotation spectra of polyatomic molecules | (PDF) |
| 24 (S) | Energy levels of a rigid rotor | (PDF) |
| 25 | Polyatomic vibrations: normal mode calculations | (PDF) |
| 26 | Polyatomic vibrations II: s-vectors, G-matrix, and Eckart condition | (PDF) |
| 27 | Polyatomic vibrations III: s-vectors and H2O | (PDF) |
| 28 | Polyatomic vibrations IV: symmetry | (PDF) |
| 29 | A sprint through group theory | (PDF) |
| 30 | What is in a character table and how do we use it? | (PDF) |
| 31 | Electronic spectra of polyatomic molecules | (PDF) |
| 32 |
The 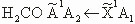
transition
|
(PDF) |
| 33 | Vibronic coupling | (PDF) |
| 33 (S) | Time-independent Schrodinger equation for a molecular system | (PDF) |
| 34 | Wavepacket dynamics | (PDF) |
| 35 | Wavepacket dynamics II | |
| 36 | Wavepacket dynamics III | (PDF) |








