Course Description
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create lumped parameter models (expressed as ODEs) of simple dynamic systems in the electrical and mechanical energy domains
- Make quantitative estimates of model parameters from experimental measurements
- Obtain the time-domain response of linear …
Upon successful completion of this course, students will be able to:
- Create lumped parameter models (expressed as ODEs) of simple dynamic systems in the electrical and mechanical energy domains
- Make quantitative estimates of model parameters from experimental measurements
- Obtain the time-domain response of linear systems to initial conditions and/or common forcing functions (specifically; impulse, step and ramp input) by both analytical and computational methods
- Obtain the frequency-domain response of linear systems to sinusoidal inputs
- Compensate the transient response of dynamic systems using feedback techniques
- Design, implement and test an active control system to achieve a desired performance measure
Mastery of these topics will be assessed via homework, quizzes/exams, and lab assignments.
Course Info
Instructor
Departments
Learning Resource Types
notes
Lecture Notes
assignment_turned_in
Problem Set Solutions
assignment
Problem Sets
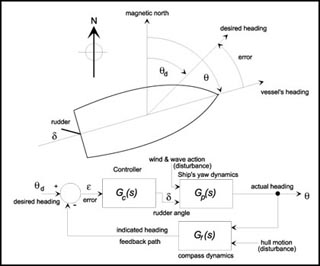
A ship’s autopilot uses dynamic feedback to adjust its heading compared to the compass setting. (Image by Prof. Rowell.)










