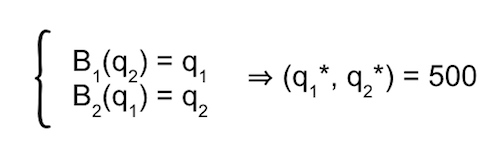Topics
- What is a game?
- Normal form games
- Equilibria
Games
Why game theory? Games on networks!
Ex. congestion, international trade, Amazon’s new office location, peer effects in school learning, deciding state taxes.
A game is a representation of strategic interaction.
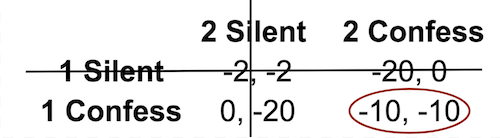
Example: Prisoner’s Dilemma
| 2 Silent | 2 Confess | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Silent | -2, -2 | -20, 0 |
| 1 Confess | 0, -20 | -10, -10 |
Example: Cournot Competition
How many iPhones should Apple produce?
- Apple produces q1 iPhones at marginal cost $500.
- Samsung produces q2 Galaxies at marginal cost $500.
- Price given by inverse demand P = 2000 — Q, Q = q1 + q
- Apple’s profit given by Pq1 — $500 * q
- Samsung’s profit given by Pq2 — $500 * q
Normal Form Games
Formally, a game consists of 3 elements:
- The set of players N.
- The sets of strategies {Si}i∈N.
- The sets of payoffs {ui: S → ℝ }i∈N.
Example: Prisoner’s Dilemma
- N = {1, 2}
- S1 = {silent, confess}, S2 = {silent, confess}
- u1 : S1 * S2 → ℝ and u2 : S1 * S2 → ℝ are given by the table, where u1 is red and u2 is blue.
| 2 Silent | 2 Confess | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 Silent | -2, -2 | -20, 0 |
| 1 Confess | 0, -20 | -10, -10 |
Example: Cournot Competition
- N = {1, 2}
- S1 = [0, ∞), S2 = [0, ∞)
- We ignore that q must be integers.
- u1 : S → ℝ and u2: S → ℝ given by
ui (q1, q2) = (P — $500)q1 = ($2000 — q1 — q2 — $500)qi
In many cases, the sets of strategies have some structure:
- Simultaneous games (penalty kicks in soccer).
- Repeated games (Libor rate manipulation scandal).
- Sequential games (how should US respond to china’s tariffs?).
What happens when there is a game-like situation?
There are many variations…
- Weak prediction: “Dominated strategies are never played.”
- Strong prediction: “Mutually optimal strategies are played.”
Elimination of strictly dominated strategies
Example: Prisoner’s Dilemma
Example: Battle of the Sexes

No elimination needed.
Equilibria
Nash equilibrium - A state with no incentive to deviate that can be sustained.
Given the opponents’ strategies, what would you do?
“Best response correspondence” Bi : S-i → Si
- Bgirl(musical) = {musical}
- Bgirl(soccer) = {soccer}
- Bboy(musical) = {musical}
- Bboy(soccer) = {soccer}
⇒ (M,M) and (S,S) are mutually optimal; “nash equilibria.”
When the best response correspondence only has one element, we may instead use the best response function (Bgirl(musical) = musical).
Example: Cournot Competition
Given Samsung’s production q2, Apple wants to maximize its profits
u1(q1, q2)=(1500 — q1 — q2)q
\n<section data-uuid=
That is, B1(q2) = ½(1500 — q2). Similarly, B2(q1)= ½(1500 — q2).
Nash equilibrium is the fixed point: